By Bruno Oliveira and EloInsights
- Master Data Management is a data management strategy.
- MDM aims to ensure the quality, consistency and integrity of critical data in an organization.
- EloGroup has developed an application architecture so that an organization can successfully execute an MDM strategy.
We know that for an organization seeking to remain competitive in today’s market, it is imperative to adopt a strategic approach to collecting, organizing, storing and interpreting data.
In other words, nowadays, it is crucial for companies to adopt a data-driven culture, in which decision-making is guided by data, thus, increasing its assertiveness and the chances of future success – both in terms of core business and new initiatives to generate value.
But a data-driven culture does not just involve capturing and storing an operation’s data in a generic way. It requires a more advanced lens, which considers specificities, such as data quality, cohesion between different bases within multiple areas of the company, the accuracy of this data and data governance, among others.
In short, it is only in this way that an organization will be able to take fuller ownership of the data produced, optimize its operations, make more assertive decisions and, in short, ensure that its use acts as a bridge to a more sustainable future for all stakeholders.
But how to do this? It is in this scenario that the concept of Master Data Management (MDM) emerges.
What is Master Data Management?
Master Data Management is a data management strategy that aims to ensure the quality, consistency and integrity of an organization’s critical data. The term “master data” refers to key data that is shared and used across various departments or systems within a company.
The MDM strategy involves maintaining data centrally, ensuring that information is accurate and consistent throughout the organization. This can include records on customers, suppliers and products, which are key to making business decisions.
MDM is crucial for companies because it allows them to maintain a single “source of truth” for their key data, avoiding duplication and the dissemination of inconsistent information. This effective management can improve the quality of business decisions, increase operational efficiency and prevent errors.
Which consequences does an organization that does not have an MDM strategy may face?
The following points help to understand the risks to which an organization exposes itself by not establishing an effective Master Data Management strategy.
- Lack of visibility and control over data: greater difficulty in controlling and managing master data, which can result in outdated, inconsistent and duplicated data;
- Difficulty in decision-making: a lack of data reliability can negatively affect company decision-making, since incorrect or outdated data can lead to inaccurate analysis;
- Increased risk of errors and compliance problems: the organization may be more exposed to errors and inconsistencies, which can lead to compliance problems with regulations and data protection laws;
- Loss of business opportunities: without an MDM, the company can lose business opportunities because it does not have a complete and reliable view of its data, which can negatively affect its ability to innovate and adapt to market changes;
- Difficulty integrating systems: it can be more difficult to integrate systems and applications that use different data sources, which can lead to compatibility and interoperability problems;
- Difficulty in scaling: as the company grows and adds new systems and data sources, manual data management can become increasingly complex and difficult to manage, which can limit the company’s scalability;
- Poor data quality: the lack of data standardization and validation can lead to poor data quality, which can affect the reliability of reports and analyses;
- Difficulty in meeting customer needs: with customer data scattered across different systems and not up-to-date and inaccurate, it becomes more difficult for the company to provide effective customer service; and
- Security risk: Master data can be scattered across different systems and locations, which increases the risk of security breaches and the leakage of confidential records.
What characteristics must an application have to implement an MDM strategy?
- Automation of capture and validation: to guarantee the accuracy and reliability of the data collected, automation techniques are used to validate and normalize the records, ensuring their integrity;
- Metadata management: aims to define and reference the elements in each domain,, creating the necessary documentation on the current elements in an organization, guaranteeing the quality of the data;
- Quality management: aims to detect and correct inconsistencies and errors in the database, ensuring integrity and consistency;
- Integration: aims to guarantee the consistency and cohesion of data between different systems, making it possible to share information between departments and improve the quality of records;
- Governance: enables the creation of policies and guidelines that increase data security, compliance and quality, defining effective procedures for managing, implementing and altering records, guaranteeing their integrity;
- Analysis and visualization aim to transform raw data into easy-to-understand information, using key indicators, dashboards and reports to effectively visualize results and make informed decisions in master data management; and
- Change log: this is a crucial functionality for data management, aimed at recording and tracking all changes made to data. It provides precise information on the changes made, including the person responsible for the change, the time of the change and the reason. This functionality is key to maintaining data integrity, identifying potential errors and correcting problems, contributing to regulatory compliance and improved governance.
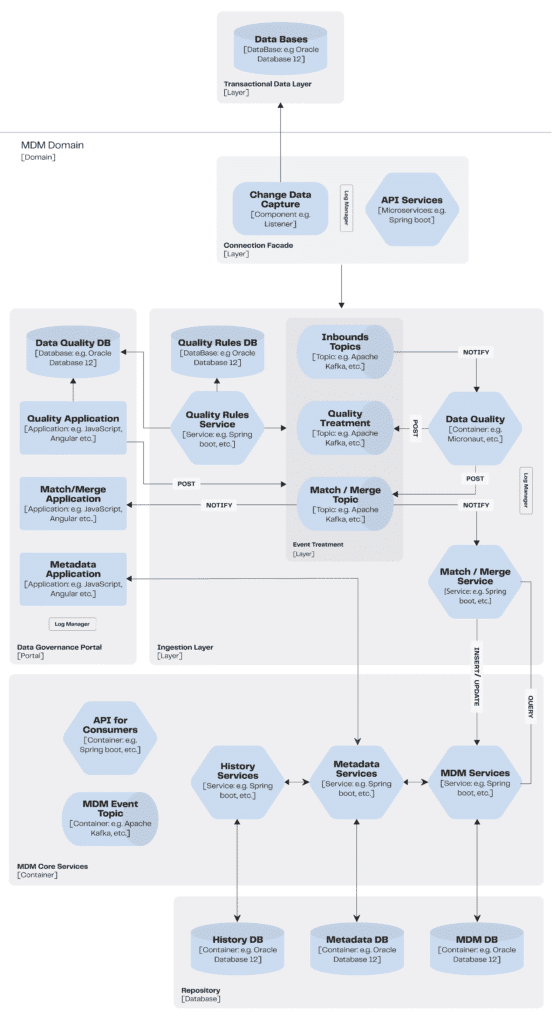
Within this context, EloGroup has developed an application architecture so that an organization can successfully execute an MDM strategy.
To ensure that the data is up to date, a process is implemented to listen to the databases where the entities are stored. In addition, rules are created to validate the quality of the data entered and a data dictionary (metadata) is created to standardize the nomenclature and definition of the terms used.
A system for storing the history of master entities is also implemented, allowing changes to be visualized and trends to be analyzed over time. These measures aim to improve the quality and reliability of the data, enabling more accurate and effective decision-making in the company.
Below we will dissect some of the main aspects of this architecture:
How does EloGroup's application architecture work for an MDM strategy?
The proposed architecture is made up of the following elements:
Connection Facade
Responsible for entering data into the MDM architecture. To do this, it was proposed to use an API or a CDC (Change Data Capture) with a listener in the strategic databases for data entry.
- API: interface layer for applications and users to enter and update master data in a standardized and secure way.
- CDC: responsible for monitoring changes to the databases and automatically updating the information in the MDM system, ensuring synchronization in real time.
This approach is expected to reduce response times when updating master data, improve its quality and reliability and guarantee a single, up-to-date view of information throughout the company.
Ingestion Layer
This is where raw data is collected from various sources, such as databases, files, monitoring systems and so on. In this layer, it is common to use event messaging to deal with the volume and speed of the data being processed.
In addition, in this layer, we can find Data Quality, Match/Merge and Quality Rules services, which are responsible for guaranteeing the quality of the data collected and preparing it for the next stage of the pipeline.
- Data Quality: orchestrates the data between topics, ensuring that it passes through the appropriate validations and that there are no duplicates in the MDM.
- Match/Merge combines data from diverse sources to create a master record or a single view of it. This service can include activities such as detecting and correcting typing errors, matching data and duplicate records. In cases of duplicates or where the service has not been able to identify the real data, it will be analyzed by the entity manager, guaranteeing its integrity in the MDM.
- Quality Rules: defines and applies quality rules, with the aim of guaranteeing data integrity, consistency and compliance with the rules and standards defined by the organization. These rules can include checking for out-of-range values, validating formats, detecting null or missing values, among others. In cases of non-compliance, the data can be analyzed by the entity’s managers to validate it manually.
These services are important to ensure that the data collected is accurate, reliable and suitable for subsequent analysis and decision-making.
Data Governance Portal
It assists in the management of data in an organization, including the establishment of policies, standards, processes and controls aimed at guaranteeing integrity, quality and security.
In relation to handling data that has not passed the automatic validations of the Data Quality and Match/Merge services, it is directed to the team responsible for its governance, which can use the Data Governance Portal to manage and take the necessary actions to correct any problems identified.
The portal can provide functionalities such as tracking quality issues, creating customized validation rules, managing correction processes and tracking changes.
- Metadata application: the process of applying metadata to data in a management system. Metadata is descriptive information about data, such as its origin, format, content, owner, creation date, etc. Applying metadata allows users to better understand the content of the data, how it has been created, manipulated and processed over time. In addition, metadata is important for data discovery and analysis, as it provides information that allows data to be searched, classified and grouped more efficiently.
MDM Core Services and Repository
This layer contains the services responsible for storing and managing the data in the MDM. These services include the MDM DB, which stores the entities with the Golden Record (a single version of all the data entities in an organizational ecosystem, also known as the “single version of the truth”), the Metadata DB, which stores the MDM’s metadata, and the History DB, which tracks and records changes to the data.
In addition, there is also the API for Consumers, which allows consumption of the information stored in the MDM, and the MDM Event Topic, which is an event topic for consumption with each change made to the MDM.
Architecture design
Conclusion
A Master Data Management strategy is key to ensuring consistency in the use of data within an organization. Through it, it is possible to keep entities up to date and ready for use, avoid duplicates and errors, and ensure that data is ready for access by the various parts of an organization. The advantages are manifold, but one of the main ones is the possibility of using this data to build a more informed, assertive decision-making culture, capable of improving operational efficiency and promoting innovation.
EloGroup offers a robust application architecture capable of successfully implementing an MDM model and putting your organization on the path to establishing a data-driven culture, capable of guiding it towards building a more efficient, innovative and sustainable future.
BRUNO OLIVEIRA works as Manager at EloGroup.











